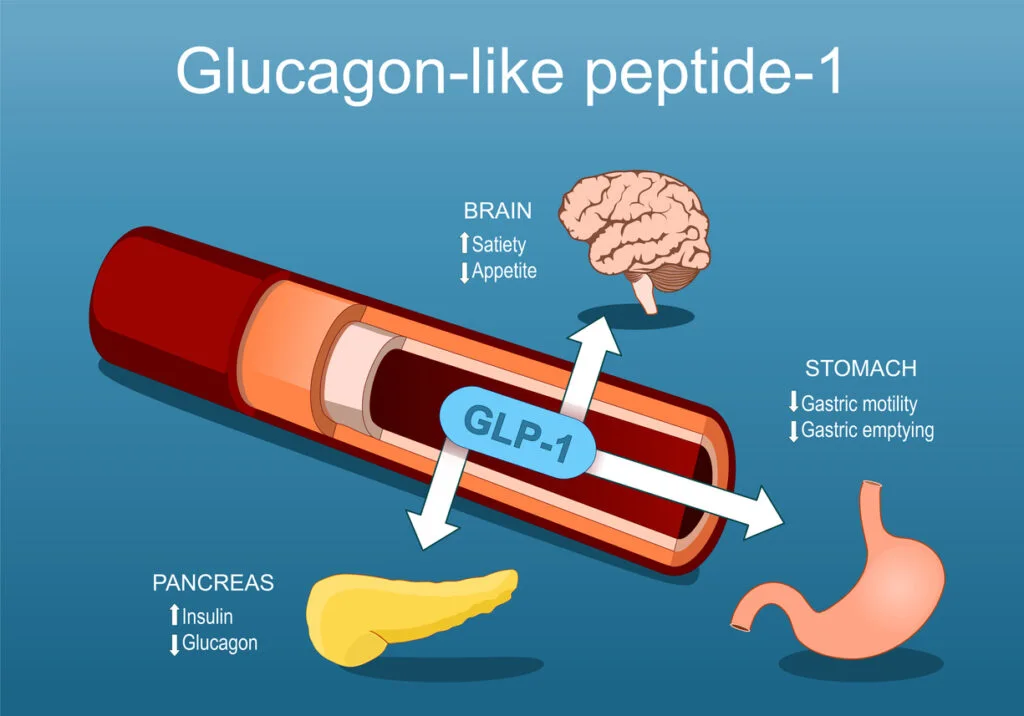
GLP-1 agonists, known for managing blood sugar and body weight, also exhibit anti-inflammatory properties. Recent studies suggest these medications may reduce systemic inflammation through mechanisms involving the brain. Research published in Cell Metabolism indicates that GLP-1 agonists can influence brain signaling pathways, leading to suppressed inflammation in other body regions. Additionally, findings in Kidney International reveal that liraglutide, a GLP-1 agonist, can decrease inflammation associated with kidney disease. These insights enhance our understanding of the broader therapeutic potential of GLP-1 agonists beyond diabetes and obesity treatment.